DevSecOps Process
DevSecOps Process Structure
The DevSecOps process is a series of automated processes and tools that help build, test, and deliver applications in production environments while securing them at every stage. Typically, companies have three main environments for project deployment: Dev, Staging, and Production. Larger companies may have additional environments such as UAT, Sandbox.
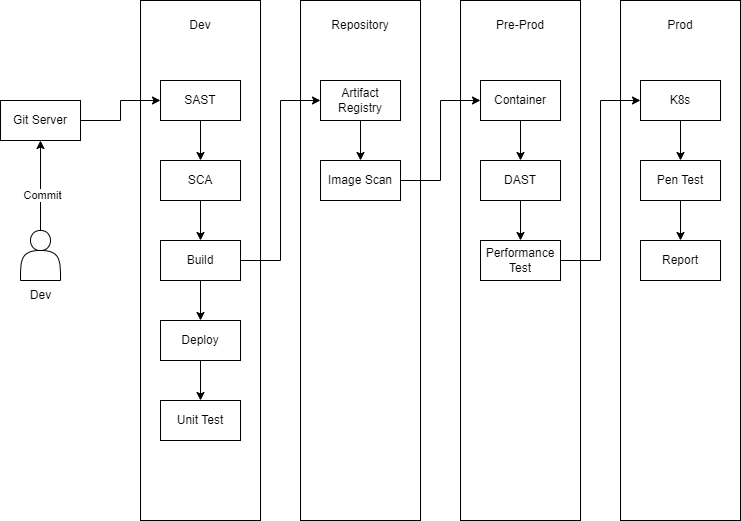
Dev (Development Phase)
- SAST (Static Application Security Testing): This is the first step in the development phase. SAST analyzes the application’s source code to detect potential security vulnerabilities. This check is performed without running the program, helping to identify security issues early in the development process.
- SCA (Software Composition Analysis): After SAST, SCA is performed to check third-party software components (such as libraries and open-source packages) used in the project. SCA helps detect known security vulnerabilities in these components.
- Build: After security checks, the source code is built into an executable application. This process may include compiling code, creating application packages, and other necessary steps to prepare the application for deployment.
- Deploy: Once built, the application is deployed to a testing or staging environment for further evaluation.
- Unit Test: At this stage, unit tests are performed to ensure that each component of the source code functions as required.
Repository (Artifact Management Phase)
- Artifact Registry: After the application has been tested and deployed, it is stored in an artifact registry. This registry holds different versions of the application, making it easier to manage and deploy later.
- Image Scan: Docker images or other deployment artifacts are scanned for security vulnerabilities. This is a security check for deployment artifacts before they move on to the next stages.
Pre-Prod (Pre-Production Phase)
- Container: The application is deployed as a container in preparation for testing before deployment to the production environment.
- DAST (Dynamic Application Security Testing): DAST is performed on the running application to detect security vulnerabilities that may only appear when the application is operational.
- Performance Test: Performance testing is carried out to assess the application’s load capacity and performance under various conditions. This ensures that the application can function well when deployed to production.
Prod (Production Phase)
- K8s (Kubernetes): The application is deployed to the production environment, typically on a Kubernetes (K8s) platform for management and operation.
- Pen Test (Penetration Testing): Penetration testing is performed in the production environment to detect security vulnerabilities that may have been missed in previous stages.
- Report: Finally, security, performance, and test results are compiled into reports for a comprehensive assessment of the application’s status before and after production deployment.